Searching Informed Search, Adversarial Search, &, Constraint Satisfaction
1. Adversarial search
bekerja dengan cara mencari berbagai kemungkinan solusi atas sebuah masalah. Ini seperti saat kita melakukan permainan rolex atau gambling (tic-tac-toe,), dimana semua kemungkinan akan kita coba. Algoritma ini sulit digunakan untuk melakukan pencarian di internet, sebab berapa banyak kemungkinan yang akan di dapat untuk mencari sebuah kata di internet? Nyaris tak terhingga.
Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Saat kita mencari suatu kata/kalimat di internet, maka algoritma constraint satisfaction search ini sepertinya adalah metode yang paling mendekati atau sesuai dengan keinginan mu. Algoritma pencarian jenis ini, akan mencari solusi dengan cara memberikan berbagai alternatif pilihan. Algoritma ini akan mencari dengan berbagai cara, dan tidak harus dengan cara yang berurutan.Itu tadi beberapa algoritma yang diperlukan saat sebuah search engine akan dibuat. Dan seringkali lebih dari satu algoritma yang digunakan oleh sebuah search engine. Dan seringkali juga, search engine tertentu akan membuat algoritma yang baru
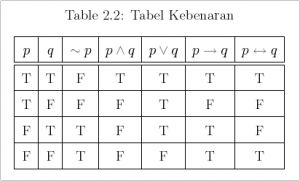
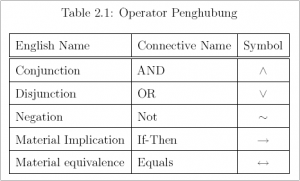
2. Propositional logic merupakan salah satu bentuk (bahasa) representasi logika yang paling tua dan paling sederhana. Dengan cara ini beberapa fakta dapat digambarkan dan dimanipulasi dengan menggunakan aturan-aturan aljabar Boolean. Propositional logic membentuk statement sederhana atau statement yang kompleks dengan menggunakan propositional connective, dimana mekanisme ini menentukan kebenaran dari sebuahstatement kompleks dari nilai kebenaran yang direpresentasikan oleh statement lain yang lebih sederhana. Beberapa operator penghubung dasar yang seringkali dipakai dalam propositional logic ditunjukkan dalam Tabel 2.1. sedangkan tabel kebenaran untuk masing-masing operator dapat dilihat pada Tabel 2.2.
Contoh :
Proposisi: Semua planet tata-surya mengelilingi matahari.
Dapat diekspresikan ke dalam bentuk:
Atau
Sentence: Every body who know Hitler, either like Hitler or think that anyone who killed some one is crazy
Proportional Logic is:
“x : [body(x) Ù know(x, Hitler)]® [like(x, Hitler)Ú (“y:$z: killed(y, z) ® crazy(x, y)]
3. Codingan untuk Algoritma A & Algoritma A* (A Star)
Langkah-langkah pencarian dalam Algoritma A*
Setelah nilai heuristik dari masing-masing node didapat maka kita akan mencari f(n) menggunakan algoritma A* dengan rumus
f(n) = h(n) + g(n) dimana,
h(n) = Nilai heuristik antar Koordinat.
g(n) = Jarak Koordinat ke titik tujuan
Contoh kodingan A*
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261
|
// Astar.cpp// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*
// Compiler: Dev-C++ 4.9.9.2 // FB – 201012256 #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include <queue> #include <string> #include <math.h> #include <ctime> using namespace std; const int n=60; // horizontal size of the map const int m=60; // vertical size size of the map static int map[n][m]; static int closed_nodes_map[n][m]; // map of closed (tried-out) nodes static int open_nodes_map[n][m]; // map of open (not-yet-tried) nodes static int dir_map[n][m]; // map of directions const int dir=8; // number of possible directions to go at any position // if dir==4 //static int dx[dir]={1, 0, -1, 0}; //static int dy[dir]={0, 1, 0, -1}; // if dir==8 static int dx[dir]={1, 1, 0, –1, –1, –1, 0, 1}; static int dy[dir]={0, 1, 1, 1, 0, –1, –1, –1}; class node { // current position int xPos; int yPos; // total distance already travelled to reach the node int level; // priority=level+remaining distance estimate int priority; // smaller: higher priority public: node(int xp, int yp, int d, int p) {xPos=xp; yPos=yp; level=d; priority=p;} int getxPos() const {return xPos;} int getyPos() const {return yPos;} int getLevel() const {return level;} int getPriority() const {return priority;} void updatePriority(const int & xDest, const int & yDest) { priority=level+estimate(xDest, yDest)*10; //A* } // give better priority to going strait instead of diagonally void nextLevel(const int & i) // i: direction { level+=(dir==8?(i%2==0?10:14):10); } // Estimation function for the remaining distance to the goal. const int & estimate(const int & xDest, const int & yDest) const { static int xd, yd, d; xd=xDest–xPos; yd=yDest–yPos; // Euclidian Distance d=static_cast<int>(sqrt(xd*xd+yd*yd)); // Manhattan distance //d=abs(xd)+abs(yd); // Chebyshev distance //d=max(abs(xd), abs(yd)); return(d); } }; // Determine priority (in the priority queue) bool operator<(const node & a, const node & b) { return a.getPriority() > b.getPriority(); } // A-star algorithm. // The route returned is a string of direction digits. string pathFind( const int & xStart, const int & yStart, const int & xFinish, const int & yFinish ) { static priority_queue<node> pq[2]; // list of open (not-yet-tried) nodes static int pqi; // pq index static node* n0; static node* m0; static int i, j, x, y, xdx, ydy; static char c; pqi=0; // reset the node maps for(y=0;y<m;y++) { for(x=0;x<n;x++) { closed_nodes_map[x][y]=0; open_nodes_map[x][y]=0; } } // create the start node and push into list of open nodes n0=new node(xStart, yStart, 0, 0); n0->updatePriority(xFinish, yFinish); pq[pqi].push(*n0); open_nodes_map[x][y]=n0->getPriority(); // mark it on the open nodes map // A* search while(!pq[pqi].empty()) { // get the current node w/ the highest priority // from the list of open nodes n0=new node( pq[pqi].top().getxPos(), pq[pqi].top().getyPos(), pq[pqi].top().getLevel(), pq[pqi].top().getPriority()); x=n0->getxPos(); y=n0->getyPos(); pq[pqi].pop(); // remove the node from the open list open_nodes_map[x][y]=0; // mark it on the closed nodes map closed_nodes_map[x][y]=1; // quit searching when the goal state is reached //if((*n0).estimate(xFinish, yFinish) == 0) if(x==xFinish && y==yFinish) { // generate the path from finish to start // by following the directions string path=“”; while(!(x==xStart && y==yStart)) { j=dir_map[x][y]; c=‘0’+(j+dir/2)%dir; path=c+path; x+=dx[j]; y+=dy[j]; } // garbage collection delete n0; // empty the leftover nodes while(!pq[pqi].empty()) pq[pqi].pop(); return path; } // generate moves (child nodes) in all possible directions for(i=0;i<dir;i++) { xdx=x+dx[i]; ydy=y+dy[i]; if(!(xdx<0 || xdx>n–1 || ydy<0 || ydy>m–1 || map[xdx][ydy]==1 || closed_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]==1)) { // generate a child node m0=new node( xdx, ydy, n0->getLevel(), n0->getPriority()); m0->nextLevel(i); m0->updatePriority(xFinish, yFinish); // if it is not in the open list then add into that if(open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]==0) { open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]=m0->getPriority(); pq[pqi].push(*m0); // mark its parent node direction dir_map[xdx][ydy]=(i+dir/2)%dir; } else if(open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]>m0->getPriority()) { // update the priority info open_nodes_map[xdx][ydy]=m0->getPriority(); // update the parent direction info dir_map[xdx][ydy]=(i+dir/2)%dir; // replace the node // by emptying one pq to the other one // except the node to be replaced will be ignored // and the new node will be pushed in instead while(!(pq[pqi].top().getxPos()==xdx && pq[pqi].top().getyPos()==ydy)) { pq[1–pqi].push(pq[pqi].top()); pq[pqi].pop(); } pq[pqi].pop(); // remove the wanted node // empty the larger size pq to the smaller one if(pq[pqi].size()>pq[1–pqi].size()) pqi=1–pqi; while(!pq[pqi].empty()) { pq[1–pqi].push(pq[pqi].top()); pq[pqi].pop(); } pqi=1–pqi; pq[pqi].push(*m0); // add the better node instead } else delete m0; // garbage collection } } delete n0; // garbage collection } return “”; // no route found } int main() { srand(time(NULL)); // create empty map for(int y=0;y<m;y++) { for(int x=0;x<n;x++) map[x][y]=0; } // fillout the map matrix with a ‘+’ pattern for(int x=n/8;x<n*7/8;x++) { map[x][m/2]=1; } for(int y=m/8;y<m*7/8;y++) { map[n/2][y]=1; } // randomly select start and finish locations int xA, yA, xB, yB; switch(rand()%8) { case 0: xA=0;yA=0;xB=n–1;yB=m–1; break; case 1: xA=0;yA=m–1;xB=n–1;yB=0; break; case 2: xA=n/2–1;yA=m/2–1;xB=n/2+1;yB=m/2+1; break; case 3: xA=n/2–1;yA=m/2+1;xB=n/2+1;yB=m/2–1; break; case 4: xA=n/2–1;yA=0;xB=n/2+1;yB=m–1; break; case 5: xA=n/2+1;yA=m–1;xB=n/2–1;yB=0; break; case 6: xA=0;yA=m/2–1;xB=n–1;yB=m/2+1; break; case 7: xA=n–1;yA=m/2+1;xB=0;yB=m/2–1; break; } cout<<“Map Size (X,Y): “<<n<<“,”<<m<<endl; cout<<“Start: “<<xA<<“,”<<yA<<endl; cout<<“Finish: “<<xB<<“,”<<yB<<endl; // get the route clock_t start = clock(); string route=pathFind(xA, yA, xB, yB); if(route==“”) cout<<“An empty route generated!”<<endl; clock_t end = clock(); double time_elapsed = double(end – start); cout<<“Time to calculate the route (ms): “<<time_elapsed<<endl; cout<<“Route:”<<endl; cout<<route<<endl<<endl; // follow the route on the map and display it if(route.length()>0) { int j; char c; int x=xA; int y=yA; map[x][y]=2; for(int i=0;i<route.length();i++) { c =route.at(i); j=atoi(&c); x=x+dx[j]; y=y+dy[j]; map[x][y]=3; } map[x][y]=4; // display the map with the route for(int y=0;y<m;y++) { for(int x=0;x<n;x++) if(map[x][y]==0) cout<<“.”; else if(map[x][y]==1) cout<<“O”; //obstacle else if(map[x][y]==2) cout<<“S”; //start else if(map[x][y]==3) cout<<“R”; //route else if(map[x][y]==4) cout<<“F”; //finish cout<<endl; } } getchar(); // wait for a (Enter) keypress return(0); } |